High commissions on financial products can be a drain for any investor. All Regulatory organizations(IRDA for Insurance, SEBI for Mutual Funds) try to disclose the commissions involved in their product. How do you find out what the commission being paid on insurance products is? This article talks about commission paid to Post office scheme, Insurance Policies (Life and Non Life), ULIPs, Commission on buying stock, Mutual Funds. This would help how can you plan your investments to make the best returns with the current commission structure. Remember Agents will sell what’s good for their pockets
What is a commission?
A commission is an amount of money that someone is paid when they sell something. It is usually a percentage of a sale that has been made. Many people work on a commission basis such as Salespersons, insurance agents. When working on a commission, a person is usually told that they will earn a certain percentage of the items or services they sell. (E.g., you’ll get 10% of what you sell). Example: Shyam works as a salesman. He has just sold say a car for 5 lakh 5,00,000. If he makes a 4% commission then Shyam has made 20,000 (4% of 5,00,000)for selling the car. That is why sales people like to sell expensive items. The more expensive the item, the more money they can make
Commissions are everywhere and you have to pay the price of transactions. Commission bearing financial products, such as mutual fund schemes and insurance policies, run the risk of mis-selling by vendors who push products that maximise their incomes, rather than client welfare. Now the market is split into chemists and doctors. The chemist simply vends financial schemes and offers no opinion on what you should buy. You will probably come to him for ease of transaction and pay commission. If you don’t want to do the homework and would rather have advice from a professional then you will not go to a chemist but to an entity that has the ability to offer financial advice like doctor. Which means, the adviser has a set of attributes in terms of a basic level of education and certification and is in a regulatory framework that allows you to trust his credentials. For this, you must be willing to pay an annual fee to the financial adviser, who may also vend the products himself or have tie-ups with pure vendors.
Table of Contents
Commission on Post office Schemes
Payment of commission to agents on PPF schemes (1%) and Senior Citizens’ Savings Scheme (0.5%) has been discontinued, with effect from 1st December, 2011
Agency commission under all other schemes (except Mahila Pradhan Kshetriya Bachat Yojana or Recurring Depsoits agents) has been reduced from 1% to 0.5%
| Recurring Deposit (MPKBY) | 4.0% |
| RD – PRSS | Discontinued from 01/10/2016 |
| 1 Year Time Deposit | 0.5% |
| 2 Year Time Deposit | 0.5% |
| 3 Year Time Deposit | 0.5% |
| 5 Year Time Deposit | 0.5% |
| Monthly Income Scheme – MIS | 0.5% |
| 5 Year NSC | 0.5% |
| 10 Year NSC – Discontinued | – |
| Kisan Vikas Patra – KVP | 1.0% |
| Sr. Citizen Savings Scheme | NIL |
| PPF | NIL |
Commission on Insurance Policies
The objective of paying Commission on Insurance Policies is to increase insurance penetration and density in the country. Life insurance policies follow a front loaded commission structure where a fat chunk of the first-year premium is paid to the agents upfront as a commission. Commission on insurance policies depends on the type of insurance such as Life Insurance, Pension, and Non-Life.
In life insurance policies agents’ commission comes under the banner of Premium Allocation Charge. This is a recurring charge, which means this is deducted on every premium you pay. Usually, charges are highest in the first year and are constant for the remaining term.
The Commission is earned by all the insurance intermediaries or middlemen such as corporate agents, insurance brokers, web aggregators and insurance marketing firms. If the policy is procured directly by an insurer, then no commission or remuneration will be paid to an insurance agent.
Only a plain quote is given for term insurance plans with no detailed benefit illustrations. The commission structure is not visible. However, consumers can circumvent this problem by comparing the cost structure of the online term insurance version from the same insurance company. Though the exact commission will not be available, you can get the cost differential.
For other products, detailed benefit illustrations are given for products that return some money at the end. The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IrdaI) brought down the illustrative rates from 6% and 10% earlier to 4% and 8% now. However, crucial part of the commission is missing from these illustrations.
As per Insurance Act, agents cannot refund the commission(even some part) to their customers so that agents don’t lure customers into buying an insurance policy.
Commission on Life Insurance Policies
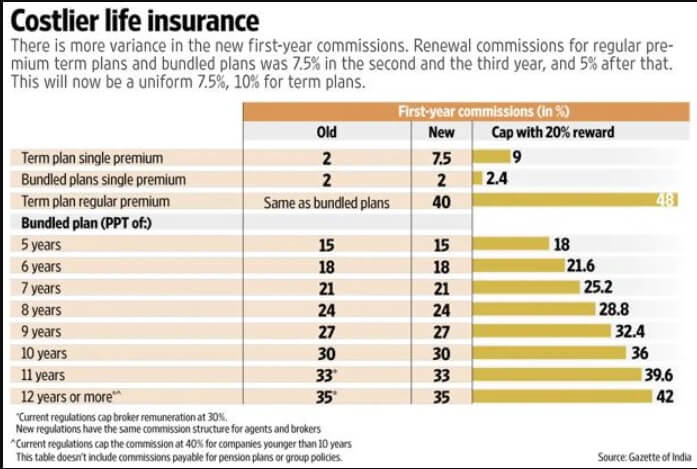
From April 2017, insurance agents will get a higher commission for selling life and non-life insurance policies. Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (Irda) has issued a notification setting the new rate of commissions to be paid to insurance intermediaries.
In single premium category, an agent will get
- 7.5% for individual pure risk products or Term Plans
- 2% for selling individual life product (other than Term plans),
- 2% for individual immediate and deferred annuity products (pension plans)
- 5% for group pure risk products. (Group Term Plans)
For regular premium products, there are two categories: pure risk and those other than pure risk or those bundled with investments.
- The first year commission for individual pure risk or term plan will be 40%, and 10% will be paid to the agent for every renewal premium.
- In the case of non-pure risk cover or for non-term plans, the commission for the policy upto five years will be 15% and will rise up to 35% for policies over 12 years.
- Apart from this, the agent will also get renewal premium, which is 7.5% every year.
- The table below shows Premium Paying terms and Commission.
- Note that highest commission payable is in case of individual term insurance. This is intentionally revised to promote the pure insurance product selling.
So, for the policy in which you premium for 12 years, an agent will get a commission of 35% in first year and 7.5% in Subsequent years.
| Premium paying terms | 1st year | Renewal Commission |
| 5 | 15 | 7.5 |
| 6 | 18 | 7.5 |
| 7 | 21 | 7.5 |
| 8 | 24 | 7.5 |
| 9 | 27 | 7.5 |
| 10 | 30 | 7.5 |
| 11 | 33 | 7.5 |
| 12 and more | 35 | 7.5 |
Let us now take an example to understand how much an agent can earn.
- The term of the plan: 15 yrs,
- Type of policy: Product-Endowment Plan i.e non Term Plan.
- Yearly Premium : Rs. 50,000. With
Calculation of Premium is as follows:
- 1 st year : 35% so 17,500
- 2nd to 15th year 7.5% of 50,000 so 3750
- Total earnings = 17,500 + 3,750 * 14 = Rs 70,000 over 15 years (before Apr 1 2017 he would have earned 17,500+ 3750 * 2 + 2500*12=55,000)
Commission on Life Insurance Policies From 1 Jan 204 to 31 Mar 2017
From 1 Jan 2014 to 31 Mar 2017 the commission was:
- Agents’ incentives have now been linked to the premium paying term (the tenor for which the policyholder pays premium regularly) of a policy.
- For a premium paying term of five years, agents will get up to 15% of the premium as commissions in the first year.
- This first-year commission will increase to a maximum of 35% in case the insurer is more than 10 years old and 40% for insurers that are less than 10 years old, if the premium paying term is 12 years or more.
In case of single premium, 2% of the single premium. In other cases, the following rates will apply.
| Premium paying terms | 1 year | 2 year3rd year | Subsequent years |
| 5 | 15 | 7.5 or 5* | 5 |
| 6 | 18 | 7.5 or 5* | 5 |
| 7 | 21 | 7.5 or 5* | 5 |
| 8 | 24 | 7.5 or 5* | 5 |
| 9 | 27 | 7.5 or 5* | 5 |
| 10 | 30 | 7.5 or 5* | 5 |
| 11 | 33/30 | 7.5 or 5* | 5 |
| 12 and more | 35/30 | 7.5 or 5* | 5 |
Note – (*)The maximum commission or remuneration:
- For brokers shall be
- (i) 30% in the first year for policies with premium paying-term of 10 and above;
- (ii) 5% in the subsequent years for all premium paying terrtis.
- During the first ten years of a life insurer’s business for all intermediaries, except for brokers, shall be 40% in first year for policies with premium paying term of 12 and above.
Commission on Pension Insurance Policies :
- In case of single premium, 2% of single premium.
- In case of other than single premium:
- 7% of the first year’s premium.
- 2% per cent of each renewal premium.
Commission on ULIP
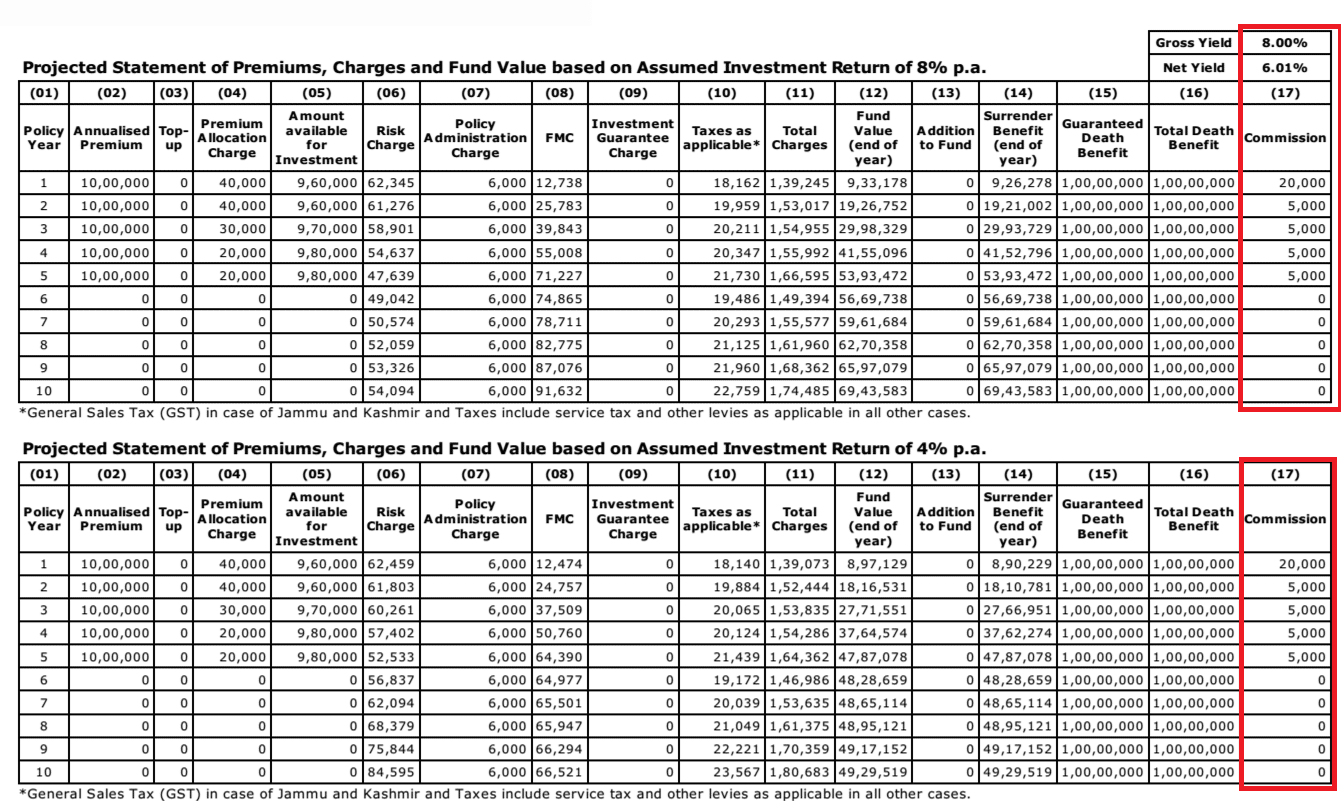
The Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) mandates all life insurance companies to provide a ‘Benefit Illustration’ (BI) to the prospective buyers of unit linked insurance plans (Ulips). The idea is to help the buyer take a look at how the premium would get invested, how and what charges would be deducted and most importantly, how the fund value will grow. It not only shows how much charges get deducted each year from the premium, but also how the investment will grow over the years.
In the BI, the underlying assumption of the gross investment return has been mandated by the regulator and currently stands at 4% and 8%. It will be shown separately running into several columns. Sample Benefit Illustration is shown below.
Remember, these calculations (based on 4% and 8% growth rates in benefit illustrations) are due to regulatory requirement and investors should not assume that this is the return they are going to get.
Commission on Non Life Insurance Policies: Auto and Health
The commission in non-life policies depends on the type of insurance.
- The maximum commission payable to an agent for Auto Insurance is 10% on the premium part paid for the own damage component of the cover only. There is no commission on premium towards third-party cover.
- In case of Health Insurance, the commission is capped at 15% of premium amount. The commission is payable at same rate on renewals also
The maximum commission or remuneration as a percentage of premium that is allowed for health insurance products offered by general insurers or stand-alone health insurers is as
| Health-Individual | 15% |
| Health-Group (Employer-Employee only) – Annual | 7.5% |
| Health-Group (Non Employer-Employee groups) | 15% |
| Health – Group (credit linked upto 5 years) | 15% |
Commission on Motor Insurance
It has increased commission structure in comprehensive or own damage motor insurance policies to 15% of the premium. This commission will be only on premium charged towards own damage(OD). Also, for the first time, it has introduced commissions on third-party motor insurance at 2.5% of the annual premium.
| Motor (Comprehensive) | 15% |
| Motor (Stand-alone TP) | 2.5% |
Commission on Fire and marine insurance
Irdai has also changed the commission structure for fire and marine insurance. In the retail fire segment, an agent will get 15% of the annual premium and 16.5% in case of an intermediary. The commission payouts in marine insurance policies and miscellaneous policies remain unchanged for agents which was 15% of annual premium. However, it has been increased for intermediaries to 16.5% of annual premium.
Commission on Stocks, ETF
When you buy a stock, you usually get charged a percentage of the trade value called as brokerage and these additional charges:
- Service tax and Cess: a 10.3% tax on the brokerage, paid to the government.
- Securities Transaction Tax (STT) : 0.125% of the trade value paid to the government.
- Stamp Duty, Turnover Charges: Regulatory fees payable to the state, exchange or SEBI, usually a small percentage of trade value
In addition, some brokers charge a demat fee per transaction and annual demat or account charges. To complicate matters further, brokerage, STT and exchange fees are different for intraday trading (buying and selling within the day), futures and options. Our article What is Demat Account : Brokerage,Charges,Comparison discusses it in detail.
Commission on Mutual Funds
Mutual Fund companies pay commission to a distributor(one who distributes or sells the mutual funds) and are of various types given below. These are paid out of the expense ratio of the Mutual funds. They are expressed as a percentage. Currently, there is no entry load system is in force which means that the investor gets the units allocated to them at the Net Asset Value (NAV) of the fund and there are no charges added to this figure. But
- One time transaction charge: It is Rs 150 for new investors of mutual fund and Rs 100 for existing investors. This is the cost which will be deducted from your invested amount.
- The upfront commission which is the amount that is received for the purpose of getting the initial investment into the fund. Upfront commission is the commission paid by mutual funds company (AMC) to agent in the first year. This is the figure that the distributor will earn immediately and is usually a percentage figure based on the amount that is brought in. Sometimes there is also a flat payment for large number of applications, especially in case of a new fund offer.
- Trail commission: This is the figure that is earned by the distributor when the investor remains with the fund for a specified period of time on a continuous basis. This payment is usually made by the fund to the distributor on an annual basis. Since these are calculated on net assets, distributors benefit from rise in his assets in the form of higher NAV of funds or sale of more units. his is most important part of commissions and main earning of mutual funds agents in long run.
The table below shows the comission earned by Mutual Fund agent in investment of a lakh each year for 15 years is 1,10,972
| No. of years | Investment | Total Asset Under Managment@12% | Upfront Commission | Trial Commission | Total Commission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rs.1,00,000 | NIL | Rs.500 | NIL | Rs.500 |
| 2 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.1,12,000 | Rs.500 | Rs.560 | Rs.1,060 |
| 3 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.2,37,440 | Rs.500 | Rs.1,187 | Rs.1,687 |
| 4 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.3,77,932 | Rs.500 | Rs.1,889 | Rs.2,389 |
| 5 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.5,35,284 | Rs.500 | Rs.2,676 | Rs.3,176 |
| 6 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.7,11,518 | Rs.500 | Rs.3,557 | Rs.4,057 |
| 7 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.9,08,901 | Rs.500 | Rs.4,544 | Rs.5,044 |
| 8 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.11,29,969 | Rs.500 | Rs.5,649 | Rs.6,149 |
| 9 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.13,77,565 | Rs.500 | Rs.6,887 | Rs.7,387 |
| 10 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.16,54,873 | Rs.500 | Rs.8,274 | Rs.8,774 |
| 11 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.19,65,548 | Rs.500 | Rs.9,827 | Rs.10,327 |
| 12 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.23,13,313 | Rs.500 | Rs.11,566 | Rs.12,066 |
| 13 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.27,02,910 | Rs.500 | Rs.13,514 | Rs.14,014 |
| 14 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.31,39,260 | Rs.500 | Rs.15,696 | Rs.16,196 |
| 15 | Rs.1,00,000 | Rs.36,27,971 | Rs.500 | Rs.18,139 | Rs.18,639 |
MF regulator SEBI says, the distributor has to inform the investor about the commission that is earned both at the time of investment as well as later on a trail basis.
Equity schemes charge as much as 2.75% (limits were enhanced in 2012, up from the earlier 2.50%) every year to its unitholders while debt funds charge up to about 2.50%. Typically equity funds pay 75-100 bps(.75% – 1%) as upfront commission and another about 0.50% as trail fees. Debt funds pay 50-75 bps as upfront charges and about 40-50 bps as trail fees. The Direct Plan has a lower expense ratio as compared to existing plans in the same schemes, as there is no commission to be paid to the distributor under this plan. Our article Direct Investing in Mutual Funds explains it in detail.
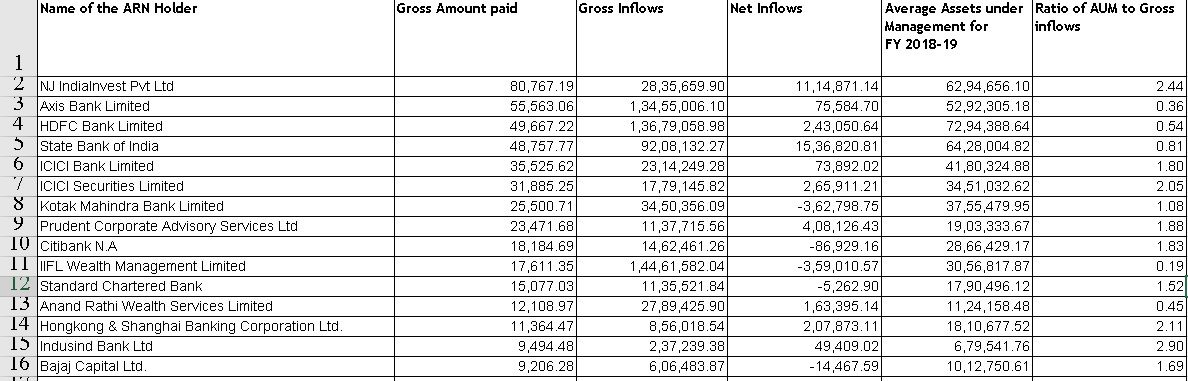
After the capital markets regulator, Securities and Exchange Board of India (Sebi), abolished entry loads with effect from August 2009, it made it mandatory for mutual fund (MF) distributors to disclose the fee that they earn from MFs. Also, as a result, distributors were also asked to charge their customers directly which some distributors do and some don’t. The commission earned by selling mutual funds by various distributors can be found at AMFI webpage commission disclosure. The snapshot of the commission paid to top distributors for FY 2018-19 is given below.
Comparing the Commission on ULIPs and Mutual Funds
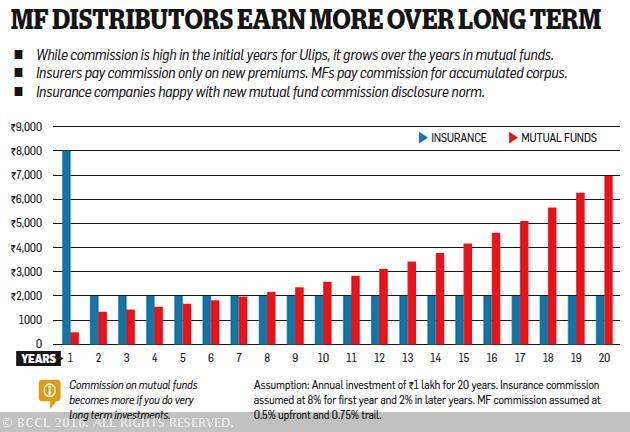
How does one compare the commission structure of mutual funds and Ulips? While the commission is high in the initial years for Ulips, it grows over the years in mutual funds. This is because insurance companies pay commission only on new premiums, while mutual funds pay commission for the accumulated corpus—the trail commission as shown in the image below.
Related Articles :
Articles related to Investing are organised at our webpage Investing some sample articles are as follows
- What is Demat Account : Brokerage,Charges,Comparison
- Direct Investing in Mutual Funds
- Beginner to Investing – Approaches, Plan, Psychology
- How Gold Ornament is Priced?
- FAQ on Tax and Fixed Deposits
As the agent’s income is directly linked to sales, he will look after his own interest rather than that of the consumer and is likely to withhold the information that may negatively impact the closure of a transaction. So what do you feel about commissions? Do you think that paying commission is justified? If yes for which product?




Where to tax commission on LIC and Mutual Funds
Tax and Commission Earned by Agents of LIC, UTI, MF, OR Post Office have to be filed in ITR3.
Out of Commission earned by the agents of above-mentioned institutions, an ad-hoc deduction is allowed in the following manner
(A) If amount of commission exceeds 60,000 in a previous year
No ad-hoc deduction is allowed. The agent can claim expenses as per provisions of section 30 to 43B of the Act.
(B) If the amount of commission does not exceed Rs 60,000 in a previous year
(i) For agents of U.T.I., Post Office and Mutual Funds …… an ad-hoc deduction of 50% of such commission is allowed.
(ii) For agents of L.I.C ……..
(a) If separate figures of first year and renewal commission are available an ad-hoc deduction of 50% of first year’s commission + 15% of renewal commission subject to a maximum of Rs 20,000 is allowed.
(b) If separate figures are not available—33 1/2 % of commission subject to a maximum of Rs 20,000 shall be allowed as ad-hoc deduction.
(c) Out of bonus commission, no ad-hoc deduction is to be allowed.
i want post office saving agency please send me renewal and first year commission rate
Do post office deduct any TDS on the commission payable to the NSC agents ? If yes please let me know the rates at which TDS is recovered.
Agency Commission is 0.5% on NSC
As per Section 194H of the Income Tax Act, TDS on commission income is required to be deducted by every person who is making the payment of such commission or brokerage.
The rate of TDS on commission income is 5% with effect from June 1, 2016. However, earlier this rate was 10%.
The surcharge, Education Cess or SHEC shall not be added to the TDS rate. Therefore, TDS on commission income will be deducted at the source rates mentioned above.
In case the Permanent Account Number (PAN) has not been quoted by the deductee, then the rate of TDS on commission income will be 20%.
The exemption limit for deduction of TDS on commission income is Rs.15000 w.e.f. June 1, 2016. However, earlier this limit was Rs. 5000.
Sir,
I am an ARN holder and I my wife is interested to invest in post office MIS and TD for 5 years about 20 laks.
Pl advise how much a postal agent can share with me for investing thru a known person for MIS 4.5 laks and TDS for 5years for 20 laks
Hi,
What does one have to do to become an agent? Is there any qualification that needs to be taken?
Also, Can one be an agent for himself ? .i.e Register as an agent at the respective AMCs, and invest his own money as an agent?
Thanks in advance
You need to study and appear for the following exam:
NISM Series V-A (Mutual Fund Distributors)
Once you clear this exam, you can apply for an ARN in your individual name by visiting any CAMS or Karvy office in your city.
Once you get the ARN and EUIN code, you need to get a tie up with any Mutual Fund house to start distributing their products and earn a commission.
Very informative article on commissions on different investment schemes I’m a recent college passout who is currently working in the industry and was thinking of investing my money wise. Thanks for sharing this article.
Very good compilation of commissions paid in the financial industry. Commissions are nothing but revenue for the middlemen. If justified there is no problem in earning a commission, in fact, it is a right of the service provider. It is prevalent in all industries especially service oriented. The problem starts when commission biases the advisory, which is bound to happen if there is a war to pay “best” commission between the product sellers.
I have invested in Mutual Funds through a Agent. So what are the advantages of investing in MFs through an agent against investing directly into Direct Mutual Funds? Kindly advise.
Asking this question itself means you know nothing about Investing or mutual funds..So you need hand-holding, understanding, and timely advice for your investments to be in place and to bear fruit..That is why you need ADVISOR for these things..Your would agree that an individual who has introduced you to the concept of investing and that too in mutual fund deserves his remuneration..that is just how it all works..
Yes Sir you are right if someone suggests the right product then that person deserves the commission.
But people are mis-sold the products because the seller sold a higher commission product.
In that case commission seems to be the problem