The relationship between person and credit card is a curious affair. People happily waive their credit card when shopping but loathe it when the credit card bill arrives. When used wisely, credit cards are a boon – an alternative of carrying cash, days of grace period, rewards, discounts. They can be the cornerstone of a sound financial strategy. But credit cards can also be a slippery slope, if caught in minimum payment trap, and you’ll tumble into the abyss of credit card debt hell, a mounting spiral of missed payments, fees, high APRs, and rate increases that will take years to recover from. Interest on Credit Card Debt is highest then all the loans. In this article we shall learn about why making minimum payments, missing due date could lead to debt.
Interest Rate Comparison of Loans
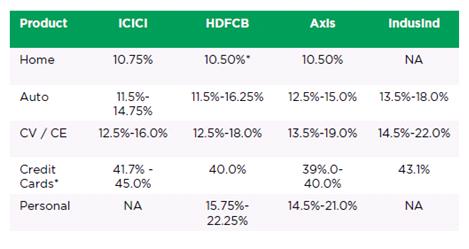
In credit cards, interest rate are called as Annual percentage rate (APR). As explained in Credit Card Fees and charges, annual percentage rate (APR) is the yearly interest rate applied to a balance carried beyond the grace period i.e it is the borrowing interest rate for when you don’t pay your bill or pay minimum amount. Credit card companies usually advertise interest rates on a monthly basis (e.g. 2% per month). For example, a credit card company might charge 3% a month, but the APR is 3% x 12 months = 36%. So when you compare Interest on credit cards you need to use APR. Comparison of interest rate on home-loans, auto loans, commercial vehicles/equipment(CV/CE) loans, Credit cards and Personal loans for different banks like ICICI, HDFC Banks, Axis Bank, Indusland bank are as follows(Src-Cardbhai: Credit Cards – Spend + APR + Portfolio Value – HDFC Vs ICICI Vs Axis Bank). As you can see Interest rate is highest for Credit Card Loans.
How does Finance charges work?
If the card-holder chooses to pay less than the total amount due, entire outstanding amount would attract called as Finance Charges. Added to it all new transactions also attract finance charges till the time all outstanding amount is paid in full. Credit Card Fees and Charges explains other charges associated with credit card. Let’s see how finance charges work through examples of making minimum payment, late fees, cash advances.
Making Minimum payment
Assuming that you have only partially paid your outstanding amount on credit card of February, and your statement is generated on 17th March for Rs. 5000.You make a payment of Rs 2000 on 25th March. And you make a purchase for Rs 1000 on 30th March. You make no further payment on your Card till 17th April. Interest rate is 2.5% per month or APR is 30%. In this example, interest levied will be as follows:
Interest calculated = (outstanding amt X interest per day X no of days)
Interest per day = (interest per month X 12)/365
Outstanding amount or balance on 17th Mar is 5000 and Rs. 2000 Rs is paid on 25th Mar. So from 17th Mar to 24th Mar balance is 5000. Interest will be charged on it as follows
On the balance of Rs 5000 (18th – 24th March) for 7 days: (30/365)*7*5000/100=Rs 28.76
As payment of Rs 2,000 was made on 25th Mar and next purchase of Rs 1,000 is on 30th Mar from 25th to 29th Mar interest will be charged on Rs 3000.
On the balance of Rs 3000 (25th – 29th March) for 5 days: (30/365)*5*3000/100=Rs 12.32
New purchase of Rs 1000 on 30th March so now balance becomes equal to 4,000. Till statement date, 17th Apr, there is no new purchase or payment so interest will be charged on Rs 4,000 from 30th Mar to 17th Apr for 19 days.
On the balance of Rs 4000 (30th March – 17th April) for 19 days: (30/365)*19*4000/100=Rs 62.46
Total Interest charged = 28.76 + 12.32 + 62.46 = Rs 103.54
You get no grace period i.e interest free credit,for your old and new purchases.
If you spend Rs.5000/- and you pay back exactly the minimum amount due(5% of 5000 i.e 250) every month and make no further purchases, then it may result in repayment stretching over 2 years 3 months with consequent interest payment on the outstanding amount. Therefore, you should, whenever your cash flow allows pay back substantially more than your minimum due. This will also help open up your spending limit & improve your credit rating. Jagoinvestor:Myth of minimum balance on credit cards also explains the concept. Let’s take another example of Mr.Sharma not paying full balance but also paying late.
Late Fees and Partial Payment
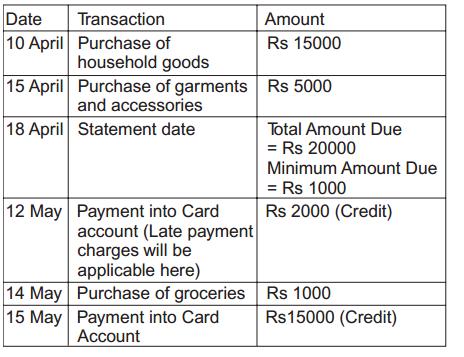
Mr. Sharma has no outstanding balance on his credit card. He uses his credit card in month of April to do following transactions. His statement date is 18th of every month and his Payment due date is 8th of next month. So for credit bill generated on 18th Apr he has to pay by 8th of May. Minimum amount due is 5% of total amount. Late charges are Rs 500. Interest charges are 3.15% per month or 3.15% X12 or 37.8% per year or 37.8/365 % or 0.1036% per day.
On 18th April Total Amount due of Rs. 20,000 (15,000 + 5,000) and Minimum amount due, 5% of 20,000, is Rs. 1000. He pays Rs 2,000 on 12th May. As he missed last date of payment he would also have to pay Late Fees and finance charges on his old and new purchases.
On 18th May his credit Bill would have late payment charges of previous month, and interest on outstanding amount of previous month and interest on the old and new charges too based on number of days. No free credit card grace period as he has not paid full amount.
Interest calculated = (outstanding amt X interest per day X no of days)
He pays Rs 2,000 on 12th May. Interest will be charged on 15,000 from 19th Apr the day he made purchase to 11th May
Interest on Rs. 15000 from 19 April to 11 May (i.e. for 23 days) = =15,000 X 0 .10356%X23= Rs. 357.29
He paid Rs 2000 on 12th May so now his outstanding amount becomes Rs 13,000(15000 -2000) and he buys groceries of Rs 1,000 on credit card on 14th May.
Interest on Rs. 13,000 from 12 May to 14 May (i.e. for 3 days) = 13,000 X 0 .10356% X 3=Rs. 40.39
Interest on Rs. 5000 from 19 April to 14 May (i.e. for 26 days) = 5,000 X 0 .10356%X23 =Rs. 134.63
He pays Rs 15,000 on 15 May. So his balance becomes 20,000-2,000-15,000 = 3,000 Rs
Interest on Rs. 3000 from 15 May to 18 May (i.e. for 4 days) = 3,000 X 0 .10356%X4 = Rs. 12.43
Interest on Rs. 1000 from 14 May to 18 May (i.e. for 5 days) =1,000 X 0 .10356%X5 = Rs. 5.18
a) Thus total Interest of = Rs. 549.91
b) Late payment charges = Rs. 500.00
c) Service Tax@ 12.36% of Interest & Late Payment Charges = 12.36% of (549.91 + 500) = Rs. 129.77
d) Total principal amount outstanding = Rs. 4000.00
(Rs 1000 fresh spend + balance Rs 3000 outstanding from last month’s billing period)
Hence Total Amount Due = (a) + (b) + (c) + (d) = 549.91 + 500+ 129.77 + 4,000 = Rs. 5179.68
Cash Advance
Finance charges on cash advances are applicable from the date of transaction until the payment is made in full. Let’s take example of Ms. Sinha. His Card Statement date is 15th of every month. Cash advance fee on his credit card is 2.0% (subject to a minimum of Rs.300 and US $7.5 at International ATMs) and finance charges are 2.5% per month or 30% APR. Minimum amount is 5% of outstanding amount.Transaction done between 16th June – 15th July are:
- Retail Purchase of Rs 5,000 – On 20th June
- Cash Withdrawal of Rs 7,000 – On 10th July
Assuming No Previous Balance carried forward from the 15th June statement, the cardholder will get his 15th July statement showing
- Rs. 12,000 of transactions
- Cash advance fee minimum of (Rs 300 and 2% of 7000 i.e 140) which is Rs 300.
- 5 days of finance charges at the rate applicable on the Rs.7,000 cash withdrawal = (7,000 * 30/365*5)/100 = Rs 28.67
- Total = Rs 12,000 + 300 + Rs 28.67 = Rs 12,328.67
The cardholder needs to make payment against the outstanding by 5th August which is 20 days from the Statement Date, for anything between the entire amount or 5% of the amount outstanding. Please note that any payment made against Credit card outstanding, would first be cleared against EMI Balance (if any) followed by Balance Transfer balance (if any), retail balance (if any) and would be adjusted against your Cash Balance (if any) last.
From the examples you can see missing payment date, paying minimum amount, cash advance are expensive and can easily lead one to debt trap. Our Credit Card Payment Calculator tells how long will it take to completely pay off credit card bill if fixed amount is paid every month. It also has calculator to find monthly payments to make to eliminate credit card balance within a certain time. Excerpt of debt trap from infographic Infographicboard : Descent into credit card is shown below
Disadvantages of credit cards
- The temptation to spend money you don’t have. They buy now without any thought as to how they’ll pay later.
- Consumers get trapped in the minimum payment mode and continuously roll over a balance for several months.
- When you default on credit card payments, you are charged with late fees and interest, increasing your debt load.
- Terms of the loan aren’t fixed. If you read the fine print of your credit card agreement, you’ll see that the lender can change your credit limit and interest rate any time. The lender is bound only to notify you in writing of the change.
- It affects your credit score. Acquiring too much credit card debt can ruin your credit score. If your credit score changes due to defaulted payments to other lenders, you become a risky borrower.
Revolving Credit
With credit card term revolving credit is often used. Let’s learn about it. Typically when one takes a loan, borrower and lender agree on terms of loan i.e on the exact amount of money borrowed, the exact amount of time to pay it back and at interest rate charged. A loan is typically repaid through fixed monthly payments. Each monthly payment includes both principle and interest. A mortgage/home loan is a example of a such a loan. If you take out a 30-year mortgage for Rs 100,000 at an annual interest rate of 8 percent, your monthly mortgage payment would be Rs 733.76. After 30 years, you would have paid back the entire Rs 100,000 plus interest (Rs 164,153). Such loans are also called closed-end credit
Credit card is an example of Revolving credit when borrowers have access to a certain amount of money that doesn’t require a final date to be paid off. As payments on the outstanding balance are made, more credit becomes available. Let’s say that you have a credit card with a limit of Rs 20,000. Using credit card you buy things worth Rs 5,000 over the course of the month, which leaves you with available credit of Rs 15,000 by the end of the month. If you pay off the full balance at the end of the month, then you are back to having Rs 20,000 in borrowing power on your credit card. Even if you can’t pay the full amount, you are required to pay at least a minimum percentage of the balance. When the next month rolls around, your statement will show the new balance plus the interest charged on the old balance. Once again, you can choose to pay it all off or pay only a portion of the balance. You’ll continue to make monthly payments on revolving credit accounts until you pay for all outstanding charges and cancel the account.
How big are credit card loans in India?
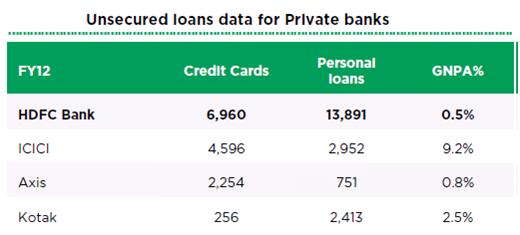
According to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) data, at the end of March 2012 the number of cards outstanding were lower at 17.65 million, compared to 18.04 million at the end of March 2011. But credit card spends jumped to Rs 96,613 crore from Rs 75,516 crore during the same period. At the end of 2011-2012 HDFC Bank had 5.6 million credit cards, For ICICI Bank,had 2.8 million, SBI and Citibank has around 2.2 million and Citibank’s outstanding cards currently stands at 2.2 million. Value of outstanding Credit Cards and Personal Loans with NPAs(Non Performing Assets) at the end of March-2012 by some of the banks are given below (figures in Rs crore). (Src-Cardbhai: Credit Cards – Spend + APR + Portfolio Value – HDFC Vs ICICI Vs Axis Bank). NPAs of financial institutions refer to loans that are in jeopardy of default
[poll id=”23″]
Related Articles:
- What happens when credit card is swiped?
- Credit Card Fees and Charges
- Bemoneyaware.com:CreditCard
- Credit Card Payment Calculator
- Chapter on Credit card basics Download (free)





how to face the harassment from the credit card executives and stop them from coming early morning to home and disturbing the complete family i asked for emi and will pay in 12 installments but they are not ready to do so and they ask for min of 20k which in this situation i am unable to pay at this position i told them to take 4 to 5k they say that r u giving us any charity and harassing literally pls give me the solution
Hello,
Adding few more detail – That will help you to decide.
Citi bank No ofCredit card holder -2765489 & No of Transaction Per month -17353642
AMERICAN EXPRESS No of credit card holder -845852 & No of Transaction Per month -3275056
HDFC Bank No of Credit card holder – & No of 8499465 and Transaction Per month -25735193
ICICI Bank No of Credit card holder – & No of 5407671 and Transaction Per month – 9862948
SBI Bank No of Credit card holder – & No of 5206379 and Transaction Per month – 10298457
Get all credit card,debit card,netbanking,wallet and UPI payment related offer & discount detail @ttps://www.pocketclue.com/