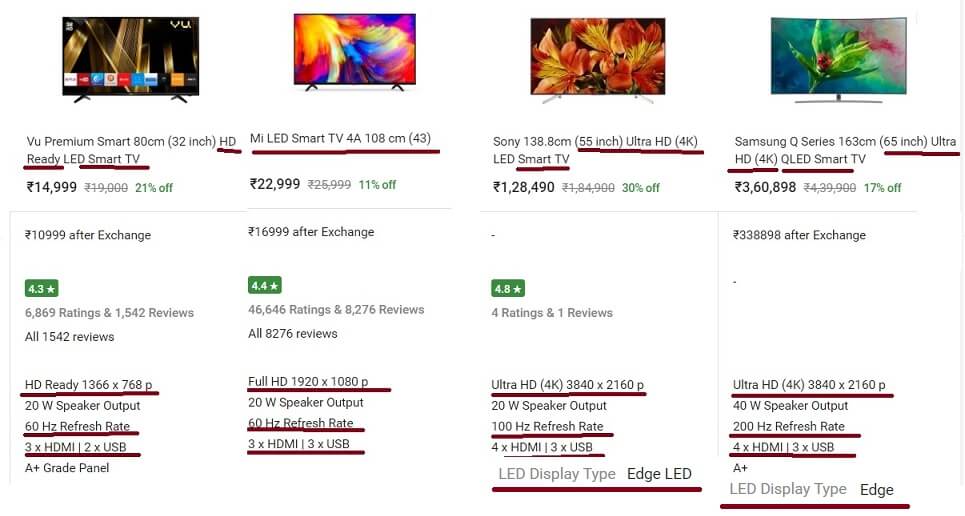
Buying a TV usually means How big it is, and how much it is? When you google you are bombarded with choices which range from 12000+ to 5 lakh rupees. Confused about whether you should you opt for 720p, 1080p, or 4K, Ultra HD? LED, OLED, What is Smart TV, Refresh Rate, HDMI? And there are a lot of terms which seem to go above the head. How good a TV picture looks in your room depends on factors other than TV technology. This article explains the terms and helps you in buying the best TV.
Table of Contents
Terminology associated with TV
Smart TV
Smart TV denotes any TV that can be connected to the internet, it comes with built-in apps for services like Netflix, Amazon Prime. Often they have web browsers, games etc. A media streamer like Amazon Fire TV Stick, Chromecast (Roku, Apple TV in the US) stream content from the Internet or local network to your TV. On a basic level, smart TV features and media streamers do the same thing (stream content), but how well they do it varies a lot. Smart TVs have operating systems and use either a wired Ethernet connection or built-in Wi-Fi to connect to a home network for internet access. There is no standard operating system or interface for smart TVs. Smart TV is unnecessary for anyone who uses a media-streaming device such as Amazon Fire Stick, Chromecast. Don’t get influenced by the number of Apps on Smart TV. For many, the only online feature that really matters, are the online streaming services such as Amazon Prime, Netflix, a Hotstar etc.
Curved TV
Curved screens, mostly used for OLED TVs and 4K LCDs, is to make the TV-watching experience more immersive. This is particularly for larger sizes (preferably 43 inches & above). They’re claimed to wrap pictures around you like IMAX, but the effect is subtle at best, and you have to sit straight on to really see it. Also, the screens can occasionally appear wrapped especially when light reflects on them.
However, not only do curved screens have no technical advantage over the other sets, but they actually have some distinct disadvantages. For one, the slightly curved aspect distorts the image and reduces the available side-viewing angles, thus limiting the best view to a few people sitting in a narrow, centre sweet spot. LED models also are less likely to produce uniform brightness across the screen.
Display Type of TV
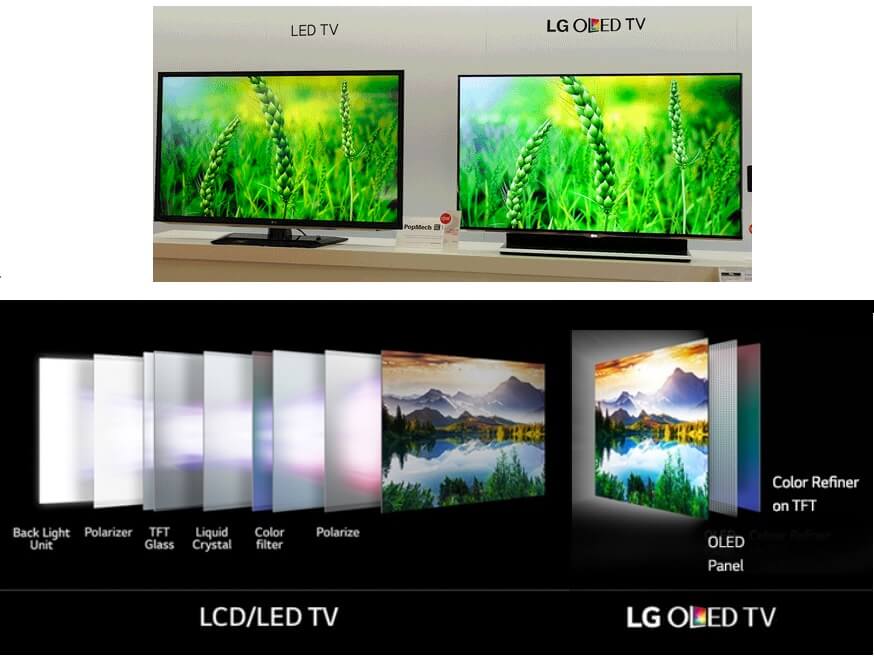
The popular TV screen types include LED(Light Emitting Diode) TV, OLED(Organic Light Emitting Diode TVs) TVs. CRT TVs are a past and Plasma TVs is dead.
You can expect to find LED TVs ranging from about 15 to 80 inches. And, in some cases, more. However, OLED TVs are only available in larger screen sizes. Usually around 55-inch to 75-inch. So the size of the screen you buy may be limited by the type of technology you want.
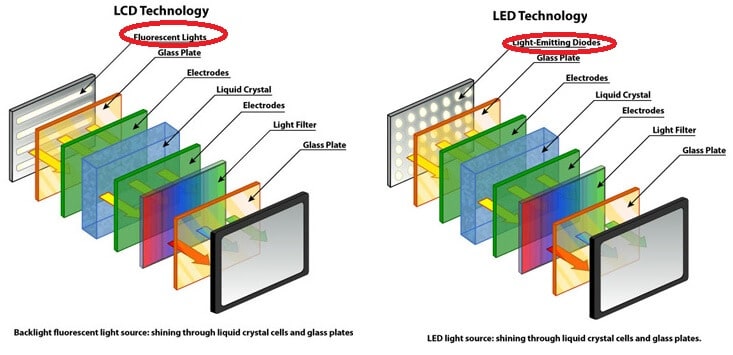
LCD or Liquid Crystal Display screen is a flat panel that can block or pass light. The Panel is made up of segments that contain blocks filled with liquid crystals. These blocks determine the colour and transparency of the television. LCD crystals don’t produce light and simply pass it, which is why these televisions have a fluorescent bulb in the back panel.
LED TVs are an upgraded format of the LCD televisions. On an LCD TV, the lamps at the back of the screen are fluorescent lamps, while LED TV uses Light Emitting Diodes(LED) to illuminate the screen the lights at the back of the screen are Light Emitting Diodes (LED) which enables the television set to be more compact and thinner.
Plasma screens: They are called Plasma because the TVs have gases injected and sealed in plasma form in between two sheets of glass. And when plugged to electricity, these gases react and cause illumination in the pixels throughout the screen! These screens are superior when compared to LED, LCD and the others. Plasma displays are disappearing from the market now because they’re more complex to manufacture than LCD HDTVs, and the technology is less readily adaptable to the higher 4K Ultra HD resolution that the TV industry is marching toward. But plasma remains a popular display technology for many serious home theater enthusiasts.
OLED (organic light-emitting diode) TVs use small organic compounds, each the size of an individual TV pixel. that light up as a specific color when fed electricity. Each diode lights up independently. Therefore OLED panels require no backlight and are thinner, lighter, require less power so more energy efficient than LCD, LED TVs. OLED TVs offer an extremely high degree of color accuracy, great contrast, wide viewing angles and a picture that is virtually blur-free. But OLED pixels differ from plasma pixels in their ability to turn off completely when called upon by the TV signal to make deep black; even at their darkest, plasma displays always stay slightly charged and emit a small amount of light so they can be ready to respond quickly to the next frame of video. OLED pixels respond so fast that they can keep up with the signal while delivering true black and infinite contrast. The difference is readily apparent in what amounts to a breathtaking, eye-popping, almost three-dimensional image that will be obvious to most viewers. OLED has other advantages as well, including good energy efficiency and the ability to produce seemingly paper-thin televisions. And OLED lends itself to both full HD 1080p models as well as the new Ultra HD resolution.
QLED or Quantum Dots LED. Quantum Dots are tiny particles, from 2 to 10 nanometers in size, with each size capable of emitting a different colour, avoiding colour filters and white LED Backlights, two things that typically limit an LCD TV colour performance. Quantum Dot technology delivers wider colour ranges than you can get with normal LCD panels. QLED TVs are generally markedly more expensive than normal LCD TVs, and Samsung is still a biggest reliable manufacture in this Quantum Dot technology,
Back Lit vs Edge Lit LED
Full-array backlights have a grid of LEDs spread out behind the panel. While Edge-lit backlights use a series of LEDs stretching along the left and right or top and bottom edges of the screen.
The vast majority of TVs today use an edge-lit backlight as instead of placing the LEDs right behind the LED panel in a full-array backlight, it allows for thinner sets and usually costs less. But, it’s more difficult to get perfectly even light across the entire screen surface with edge lighting, so many models display some subtle streakiness or hot-spotting.
TVs with a well-designed full-array backlight are expensive than the best edge-lit models, though the price for this feature continues to drop.
Panel technologies
There are two types of LCD panels used in LED-backlit TVs today: In-Plane Switching (IPS) and Vertical Alignment (VA). While they are both Liquid Crystal Display types, there are many differences between the performance of these two technologies.
IPS panels offer slightly wider viewing angles than VA panels, but struggle with contrast. On the other hand, VA panels feature narrower viewing angles. But generally, produce much better contrast.
VA technology is far beyond IPS panels when it comes to contrast. Blacks are far darker, and it shows. When in a dark environment, blacks will appear gray on IPS TVs, substantially diminishing the experience. VA contrast ratios usually range from 3000:1 to 6000:1, IPS are more in the surrounding of 1000:1. Because of this, VA LCDs will always top our Movie ratings, only surpassed by OLEDs. This only impairs the dark room performance, though, since the difference is far less visible in a bright environment.
Screen resolution of TV: 720p, 1080p, 4K
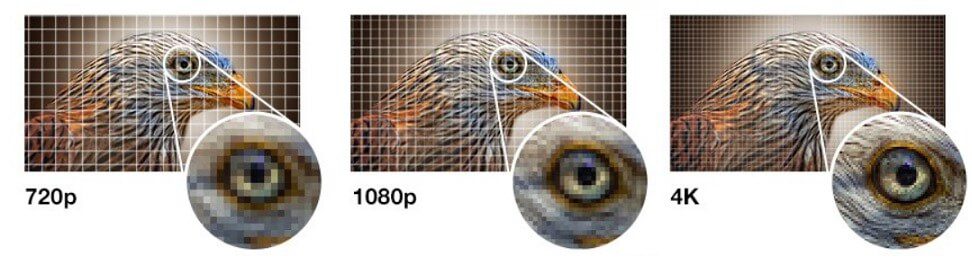
Screen resolution describes the number of fixed picture elements or pixels used to create the image. It is typically listed as a number such as 720p, 1080p, 4K and 2160p (commonly referred to as 4K Ultra HDTV) etc. Since each pixel is responsible for displaying a part of the incoming image, the more pixels you have the more precise and clear the image will appear. The more pixels on a display, the greater it’s ability to show fine details for an image. If we divide the TV screen into rows and columns then the resolution is given by the number of rows of pixels X number of columns, so TV with the screen resolution of 1920 X 1080 has 1920 rows across x 1080 pixels vertically.
The number of pixels in a TV’s display affects its sharpness, generally, the more pixels the sharper the image.
- 480p resolution is made up of 640 x 480 pixels
- 720p or High-definition is made up of resolution of 1280 x 720 pixels. The number 720 stands for the 720 horizontal scan lines of the image display resolution
- 1080p or Full HD has a grid of 1,920 pixels horizontally by 1,080 pixels vertically. In total, this means it has 2,073,600 individual pixels (1,920 x 1,080).
- HD Ready: Depending on the design of the screen, and the shape of the pixels (they can be round, square or rectangle), you may see other resolutions for HD flat screen TVs such as 1280 x 720, 1366 x 768 or 1024 x 768. A 1920 x 1080 resolution screen is referred to as ‘Full HD’, whereas an ‘HD Ready’ screen will generally be the be the lower resolution screens – 1280 x 720 or 1024 x 768.
- 4K or ultra high-definition (Ultra HD) made up of 3840 pixels and 2160 lines (3840 X 2160) and so 4 times the resolution of 1080p -a total of 8,294,400 pixels to be precise. Technically, “4K” means a horizontal resolution of 4,096 pixels. Ultra HD TVs aren’t technically “4K” since their resolution is 3,840 x 2,160. However, it doesn’t matter. 4K is way easier to say than 2,160p or Ultra HD. The picture on a 4K Ultra HD TV looks incredibly detailed.
- 8K follows the same logic, it’s twice the horizontal and vertical of 4K TVs: 7,680 x 4,320. We’re a long way away from 8K TVs being anything close to mainstream.
Contrast Ratio
Contrast ratio basically describes the range of brightness levels that your TV can display, it is the calculation of the difference between a screen deepest black and brightest whites, written for instance as, 10,000 to 1. The higher the contrast ratio, better the display when it comes to showing colours and other image details. However, most manufacturers have their own way to measure contrast ratio.
Input Ports
The standard digital input for modern home entertainment gear. Be sure to select a TV that has sufficient HDMI inputs for all your devices (unless you plan to use a home theater receiver.)
HDMI or High Definition Multimedia Interface is a way to connect a source of video to your display (TV or Monitor). As opposed to other connectors it has the advantage of being able to transfer both video and audio through the same cable. HDMI transfers data digitally—without compressing or distorting the information so it delivers the highest-quality picture and sound. You can even plug a streaming device like Amazon Fire TV Stick to turn your old TV into a smart TV.
Refresh rate
Refresh rate means how many times the picture on the screen gets refreshed in a second. Higher refresh rates create a smoother flow between images and reduce motion blur, which is handy if you watch a lot of action movies. The refresh rate is measured in hertz, so you might see 60Hz, 120Hz, or even 144Hz for a TV. The standard refresh rate is 60Hz, which means 60 times every second. But some fast-moving scenes may appear blurry in TVs with 60Hz refresh rate. Try to go for a TV with higher refresh rate as it will make the video appear smooth, letting you see content with more detail. High refresh rates can also be good for gaming.
TV’s refresh rate might not always match the refresh rate of the content you are viewing. If you’re watching a show at 30 frames-per-second, or maybe playing a video game at 60 frames-per-second, on a 120Hz TV, the TV will have to do something to fill in the gaps. Some TVs will do what is called interpolation, which creates an image that fits between the images it’s given, effectively multiplying the frame rate of whatever you’re watching. Sometimes this feature is desirable, other times it creates an odd effect that makes the video too smooth and seem more like a soap opera than a feature film. Keep an eye out for features with the words “smooth,” “motion,” or “scan” in them, as that will likely indicate interpolation
Standard Broadcast, HD Channels
Technology, over the years, has bettered the television. Be it the evolution from traditional “box TV sets” to LED, OLED screens or the way content is shot and transmitted.
SD or standard definition is the normal/standard feed that one gets on TV. The resolution of SD is 720 x 576 pixels. It doesn’t require a special TV set etc.
HD Channels
Now HD channels are also available. HD is an acronym for ‘high-definition’. Here, the picture on the screen is sharper, clearer has more details and higher resolution. HD channel can be viewed only if the consumer has an “HD” TV, HD-supportive set-top-box, and if the broadcast signals are in HD. The content is shot, edited and transmitted in HD. There are 49 HD channels in India. The resolution of HD is 1920X1080 pixels. This means the clarity of the video in HD is almost 5 times better than that of SD.
The first feed of HD, in Europe, began in the 1990s. In the US, it started in 1998. The first full-fledged HD movie channel in India was launched in 2010 by Times Television Network – Movies Now.
HD is important when it comes to viewing movies and sports. For instance, a Transformers or Titanic in Hollywood or a Zindagi Milegi Na Dobara in Bollywood will have a far better visual impact if viewed in HD. It is the same for cricket or football.
Higher satellite bandwidth is required for HD channels and an HD broadcast requires more investment from the channel.
SD channels range from Rs 4 to Rs 22 a month in terms of their price set by TRAI (Telecom Regulatory Authority of India). The authority doesn’t govern prices for HD channels since it does not come under “essential commodities”. Companies can decide the price at which they want to sell their HD channels. Typically HD channel would be more than Rs 30 per month.
True HD broadcast is usually accompanied by Dolby Digital 5.1 surround sound which gives the viewer – equipped with a home theatre – an immersive experience and helps complement the richer visuals.
- TrueHD or Full-HD is when everything – from shooting, to editing, to sending signals – is done in HD.
- In Upscaled HD, an SD feed is converted into HD.
- An HD-Ready channel is one that can accept an HD signal, provided it was given by an external device. These TVs do not have in-built HD tuners.
The equipment for the shoot of HD is different and more expensive than that used for shooting a normal SD programme. Production costs increase. Even the make-up cost increases. Since HD gives a clearer picture, the details of the skin and hence make-up is more visible on-screen.
HD Images
One of the best quality high-definition resolution images is known as 1080p. This is common in Blu-ray players, by the Sony Playstation 3/4, Xbox 360/One and Wii U games consoles or by some streaming services such as Netflix, Amazon Prime Video and YouTube.
This image will be recorded with 1920 horizontal pixels and 1080 vertical pixels of information. The result is over two million pixels of resolution which means it will be much sharper and clearer than the 480i image – which only has 307,200 pixels of information. The ‘p’ means that the image is also recorded using progressive scan, which results in a better image quality than with interlaced scan.
Ultra high-definition 4K resolution images are known as 2160p. A 4K image will be recorded using progressive scan and have a minimum resolution of 3840 x 2160 pixels – so 8.3 million pixels with a 16:9 aspect ratio. The source of 4K content is very limited at present.
Image Resolution vs Screen Resolution
Image resolution is not the same thing as the resolution of the TV The image resolution is the number of pixels in the picture that is being broadcasted. Unlike the fixed resolution of a TV, the image resolution can be different depending on how it is recorded and transmitted.
Just remember most of the images you watch on your 1080p screen will not be transmitted in 1080p, and so they will have to be processed by the TV to display properly. Similarly, you may have a 4K TV but most of the images you watch will not currently be transmitted in Ultra HD.
When the image resolution is different from the resolution of your TV, your television will scale the image to fit the screen. This scaling is performed better by some TVs than others – and this will have an effect on the quality of the picture you see. Because there are limited sources of 4K content, you may find that other factors are more important than the screen resolution.
Interlaced and Progressive Scan
The progressive scan produces a better quality of the image because the picture is created by drawing each frame of the image in one pass down the screen – from line one to line 1080. This produces a very stable and clear picture.
The resolution of a 1080i image is the same as 1080p, so each frame has a horizontal resolution of 1,920 pixels and a vertical resolution of 1080 pixels. Therefore, it can also be called ‘Full HD’. The big difference is in the letter at the end – the ‘i’. A 1080i image is transmitted as an interlaced scan picture, which means each frame of 1080 lines is actually drawn in two passes. First, all the odd lines are drawn – from 1 to 1079. Then all the even lines are drawn – from 2 to 1080. Each of these passes is known as a field – and so two fields (of 540 lines each) make up one frame of 1080 lines.
Therefore, with an interlaced image, it takes slightly longer for our eyes to see a full frame when compared to progressive scan. So although a TV does this drawing process pretty quickly (around 60 times per second), our eyes can often detect this as a slight flicker or unstable image. This method is used because it takes less bandwidth to transmit an interlaced image than a progressive one.
Most terrestrial, cable and satellite HDTV transmissions either come in 1080i or 720p formats, and so the TV will either have to de-interlace (for the 1080i) or upscale (for the 720p) in order to display them on the screen. Either way, both of these processes can affect the quality of the image you see – and how good these sources look on your 1080p TV are more dependent on the quality of the transmission and the processing in the TV, rather than its native resolution.
| Name | Alt. Names | Columns Width in pixels |
Lines Height in pixels |
Common Media |
| 576p | Standard | 720 | 576 | DVD Standard Channels |
| 720p | HD HD Ready |
1280 | 720 | HD channels (some are 1080i) |
| 1080p | Full HD FHD |
1920 | 1080 | Blu-ray Game consoles |
| 4k | 2160p Ultra HD UHD |
3840 | 2160 | Streaming Blu-ray 4k gaming |
Viewing Distance from TV
The common TV panel sizes available today are 32, 40, 42, 46/49 and 55 inch. Just because you can buy a 55-inch TV doesn’t mean you should buy it. Main factors determining the choice of the TV diagonal: a distance from the viewer to the screen and its resolution.
Remember, TVs are measured diagonally. So a 42-inch screen measures 42 inches from one corner to the opposite corner.
You have to consider the resolution of the TV. That’s because the higher the resolution, the closer you can sit before you’ll notice pixelation in an image. That means you can sit closer to a 4K TV (3840 x 2160) than you could a 1080p TV
Recommended distance for viewing 4K TV is 1.5 times of the TV vertical screen size. It means that pixels effectively disappear when viewing 4K images. This creates the impression of watching TV pictures with the same detail and resolution as real life.
| 55 inch | 1 meter / 3.28 feet |
| 65 inch | 1.2 meters / 3.94 feet |
Recommended distance for viewing High Definition TV is 3 times the TV vertical screen size.
| TV Size | Viewing Distance Range (Approx.) |
| 22 inch | 80 cm / 2.62 feet |
| 26 inch | 1 meter / 3.28 feet |
| 32 inch | 1.2 meters / 3.94 feet |
| 40 inch | 1.5 meters / 4.92 feet |
TV Market in India
There are about 70 TV brands in India. Xiaomi, Thomson and TCL have already taken the price war to market leaders Samsung, LG and Sony who control almost 70% of the Indian TV market. Prices on average have already crashed by 40%. Few examples of the price war in the TV market are:
- A 32-inch HD ready television sold for Rs 13,500 in 2016, for that price now a consumer can buy a similar sized, full HD smart TV. A TV with those specifications retailed for Rs 28,000-29,000 in 2016.
- A 43-inch, 4k smart TV is selling for around Rs 30,000 now; its price two years back was Rs 45,000-50,000.
- And a 55-inch, 4K smart TV will cost a consumer Rs 45,000-55,000 now, a steep drop from Rs 70,000-80,000 price range just two years back.
- Samsung in Jul 2018 dropped TV prices sharply after reducing prices for some older models in June. Panasonic too dropped prices on a few models above 40 inches in Aug 2018.
- 43-55 inch screen sizes are growing at a fast clip and already accounts for 30% of the Rs 22,000-crore market, and sales in the 32-inch segment are losing steam.
Price drop in 32 and 43-inch sizes has been possible in last two years due to the surplus capacity of television panels in these two sizes with consumers in the West moving to larger screens. Similarly, right now there is not much demand for the 50-inch segment which could make prices more competitive,
Among leading TV brands to enter the Indian market in the last one year are Xiaomi, TCL-owned iFFALCON, Thomson, Skyworth, Sharp and Akai. Large Chinese players like Gome and Metz are waiting in the wings.
The online explosion in the Indian TV market has actually created many brands driving price war in the 24, 32 and 43-inch screen sizes. And now, the price war will open for larger screens.
These TV makers have borrowed the playbook from Chinese smartphone brands. Chinese smartphone companies have managed to grab market share from Samsung and Micromax by selling competitively priced, specification-rich phones. Those phone makers now control more than 60% of the Indian market. The television market in India, especially in the Rs 25,000 plus segment, is not as commoditised as smartphones are and consumers will not compromise on the brand when buying a large screen model
Online television sales now account for almost 14% of the total market compared to 3-4% in 2016 when the first wave of price aggressive brands entered the market.
Which TV to buy?
It’s difficult to come to a definitive verdict. OLED clearly has the advantage in terms of image quality and appearance but they are expensive. LED, 4K LED screens are cheaper and still produce amazing images.
- Buy a Full HD TV 1080p TVand, not 720p HD Ready TVs. You would have to subscribe to HD channels or buy Streaming devices.
- Stay away from cheap Smart TVs. With several Media streaming devices such as Amazon Firestick, it makes very little sense to buy an affordable Android TV. Don’t try to find the luxury of more features within a tight budget from brands unheard of, as the entire experience might end up becoming bitter.
- The advantages of 4K become more apparent as the screen size gets larger – so if you’re after a 65-inch plus screen, our money would definitely go to 4K.
- However, if you’re after a 55-inch screen, it depends on how big your living room is. If you sit very close to the television then 4K might be your best bet – but if you’re further away, OLED will offer a better experience.









My viewing distance from our 50 inch will be 200″ eye level distance will be 40″ what would the mounting height be? I can’t seem to figure it out. Help please! Lol
I found it interesting how you mentioned how satellite television is able to transmit in Full-HD and even 4K resolutions. A friend of mine wants to start watching programs in 4K because of how realistic it looks but he has been confused about where to start. I will be sure to pass this on to him so he can look into upgrading his existing satellite service to get the best streaming service possible!