For properties sold after 1 Apr 2017, to calculate Long term capital gain on sale of property one would need to use the cost inflation index numbers available from the financial year 2001-2002. Many people who have purchased or inherited property that was purchased before 2001, often question on how to find the indexed cost of acquisition of a house. The shift in the CII base year from 1981 to 2001 will drastically change the final capital gains amount from the property. If the property has been acquired by the original owner before 1 April 2001, while selling the property owner has to find the fair market value of the property as on 1 April 2001. This article explains what is Fair Market Value, How can one find the Fair Market Value or FMV, Why was the base year changed from 1981 to 2001 and how does it results in tax saving for properties purchased before 2001. It then talks about Registered Valuer and how they determine FMV.
Table of Contents
What is Fair Market Value?
From FY 2017-18, changes in calculation of Long-term capital gains for property are
- The period of holding to qualify for long-term gains has been reduced to 2 years from 3 years.
- The base year for calculating indexed cost has been changed from 1981 to 2001.
For properties purchased before 1 Apr 2001, the latest cost inflation numbers start from 1 Apr 2001, one needs to first arrive at what is commonly known as Fair Market Value (FMV) of the property as on April 1st, 2001. FMV answers the question as to What would the property purchased in 1997 be worth on 1 April 2001? Calculating the capital gain based on any arbitrary FMV can land an assessee in trouble if the assessing officer (AO) has a different opinion or doubt over the declared value.
Fair Market Value or FMV is needed when you want to buy a property or for Sale and Purchase, Refinancing, Legal purposes, Loan purpose, Stamp duty collection, Portfolio Management, Family Law/Matrimonial or Market Valuation. FMV facilitates in establishing the right purchase price. It saves you from being overcharged. You get the real value for money. Consider another situation when you want to get a loan on the property. If the property isn’t correctly valued, you might not get a loan from the banks.
As per Income tax Guidelines for Immovable properties of 2009
Market value is the price that a willing purchaser would pay to a willing seller for a property, having due regard to its existing conditions, with all its existing advantages and its potential possibilities when laid out in its most advantageous manner.
Fair Market Value is the estimated price which any asset in the opinion of Valuation officer would fetch if sold in the open market on the valuation date.
The terms “Market Value” and “Fair Market Value” are synonym except for the word “Fair” introduces an element of a hypothetical market. The expression “if sold” does not contemplate actual sales or actual state of market. The expression “Open Market” does not contemplate a purely hypothetical market exempt from the restriction imposed by law. The fair market value excludes sentimental value advertisement, brokerage, stamp-duty, commission etc. for affecting the sale transaction.
How to find Fair Market Value or FMV?
According to the Income-tax Act, 1961, FMV shall be the higher of the cost of acquisition of the property or the price that the property shall ordinarily sell for if sold in the open market. There is no fixed formula to calculate FMV of a property. The techniques that are used to calculate FMV are given below. Remember Fair Market Value needs to be really fair!
- Find out the average sale price of similar properties in the neighbourhood, which were sold in the year 2001.
- It happens to be a very crude method of estimation. It may or may not give your correct results. Given that real estate is a heterogeneous market, in which properties can vary a lot, even within the same locality, it is difficult for an individual to determine the FMV of a particular apartment or a house, that too, for a date many years ago
- Look at circle rates or Guidance Value. Circle rates mean the minimum rate of property that is prescribed for a particular area. The circle rates are fixed by the state government or the local development authority. It becomes a reference point for estimation of stamp duty and registration charges. The authorities keep revising the rates periodically to match the changed circumstances.
- Circle rates are usually lower than the prevailing market value
- The concept of circle rates came into existence for the first time in 1999 in Bihar. In other places like Delhi, it was adopted in 2007.
- One can also consider real estate indices, such as the National Housing Bank’s (NHB’s) Residex, and two indices of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)—Housing Price Index (HPI) and Residential Property Price Index (RPPI). These indices give an idea about the prevailing pricing trends in various cities. The indices are updated quarterly based on the revenue department’s transaction data.But the utility of these indices is limited.
- Take help of a registered valuer. Recommended.
- Government-approved valuers follow a standard process for the valuation and provide a detailed report.
- In return for a nominal fee, they estimate the real worth of the property. They usually consider factors like dimensions of the property, freehold/leasehold, restrictive covenants (if any), whether insured or not.
- In case of any enquiry, the income tax department will consider the value stated in the valuation report from a registered valuer
Why was the base year changed from 1981 to 2001?
The base year earlier being used was 1981.
- There has been a considerable hardship in determining this fair value since it depends on a period which is more than three decades old.
- Property prices appreciated at a much higher rate between 1981 and 2001, compared to the increase in CII or inflation
On the properties purchased before 2001, the owners are going to have significant savings on tax incidence, an overview of which is given below. Our article Change of base year impact on Capital gains explains it in detail.
Example of Calculating Long-Term Capital Gains for Property that was purchased before 2001
Say one bought house in 1975 for 1 lakh and sold it 2017 for 1.5 crores. If one considers Fair Market in 1981 then it would be around 2.31 lakhs and its indexed cost to be 26,02,193 and in 2001 it would be 37.85 lakhs and its indexed cost to be 99,97,389. Moving the base year from 1981 to 2001 results in saving of capital gain tax of more than 15 lakhs.
| Description | 1981 | 2001 |
| Fair Market Value | 2,31,306 | 37,85,678 |
| Indexed Cost of acquistion | 26,02,193 | 99,97,389 |
| Selling price | 1,50,00,000 | 1,50,00,000 |
| Long Term Capital Gains(Rs) | 1,23,97,807 | 50,02,611 |
| Long Term Capital Gain Tax (20.6%) | 25,53,948 | 10,30,538 |
Registered Valuer to determine FMV or Fair Market Value of Property
It is advisable to get the valuation of the property done from the registered valuer. Assumptions of any type for consideration of value shall not be entertained by the income tax department. In case of any enquiry, the department will consider the value stated in the valuation report from a registered valuer. Typically, a valuer takes 3 to 4 days to prepare a valuation report
Government-approved valuers follow a standard process for the valuation and provide a detailed report. In addition to other parameters to derive at the FMV of a property, a valuer also considers area and dimensions of the property, is it freehold or leasehold, is there any restrictive covenant in regard to use of such property, insurance of the land and property, if the land falls under any development plan of the government.
A valuer needs to be registered under section 34AB of Wealth Tax Act, 1957, to act as a recognized valuer of income tax department. Each valuer is provided with a license from the department to work as a valuer. Fee and charges that a valuer can charge are also prescribed under the Act, and depend on the value of an asset. For instance,
- for first the Rs5 lakh of asset value, fee would be 0.50% of the value.
- For next Rs10 lakh, it would be 0.20%,
- for next Rs40 lakh 0.10% and 0.05% of the value thereafter.
In case Income Tax Assessing officer(AO) raises any doubt over the report it is valuer responsibility to reply, and if needed, the valuer can even visit the AO for clarification on the report
An assessee should keep the valuation report along with other documents related to capital gains, for at least 8 years after the relevant assessment year.
How to find Registered Valuers?
Typically its word of mouth or search in google. Many companies like governmentapprovedvaluers.com do it in Delhi and ZippServ in Bangalore, Pune.
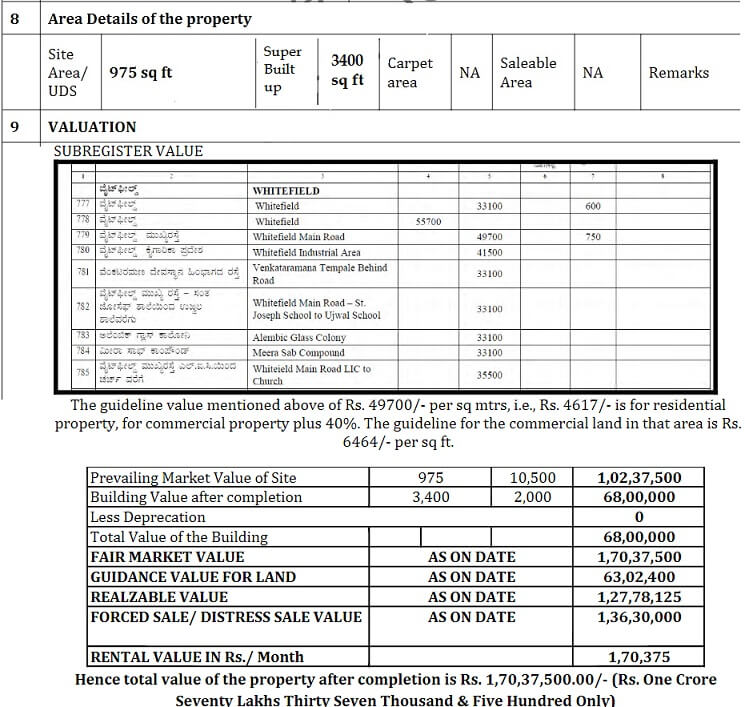
Excerpt of Sample report of a valuation of the property is shown below. This is Excerpt from sample report by ZippServ.
Related Articles:
- Cost of Inflation Index from FY 2017-18 or AY 2018-19 for Long Term Capital Gains
- Capital Gain Calculator from FY 2017-18 with CII from 2001-2002
- Cost Inflation Index,Indexation and Long Term Capital Gains
- Change of base year impact on Capital gains
- How to show Long Term Capital Gains on sale of House in ITR
Estimating the true Fair Market Value is vital from all the legal angles. Before entering into any real estate matter, make sure that your property is fairly valued.




Please contact me for get the valuation of properties for the purpose of capital gain tax, I am the government approved valuer.
Mail id- parmarronit1@gmail.com
Contact- 9601314578
In July 2019, I sold a small piece of residential land (83.6 sq mts) in Sector 5 (Part 6), Gurugram, Haryana, which was allotted to me by HUDA in February 1990. Now, I have to file ITR-2 after proper Indexation work and arriving at a Fair Market Value (FMV) of the plot as on 01-04-2001, for availing applicable Tax relief under LTCG. If you are a Govt. approved /Registered Valuer, and can provide me a detailed FMV report for the sold land, then please advise me accordingly. Thanks.
PC Pande
If the property sold in 2017, why indexation cost done till 2001.It should be donee for 2017 as indexation cost is revised every year
Indexation is reset by Govt.
Indexation is done for year of purchase.
If the property is purchased before 2001 then one would have to get the property valued and the Fair Value of the Property needs to be found as of 2001.
Explained in detail in the article http://bemoneyaware.com/fair-market-value-calculating-capital-gain-property-purchased-2001/
i purchased a property in July 1995 for Rs 6.0 lakhs, can you please advise me how do I determine the value of the property on 01 April 2001
Please get it evaluated by a property evaluator.
What is the validity of the registered valuers report in case of immovable property? Do any one need registered valuer for valuation of immovable property for FMV as on 01.04.2001?
what is the fair market value as on 01-04-2001, for a plot of land purchased in Kolkata in 1958-59 by Rs1000
Whom to approach to know the Fair market value in 2001-02 of a immovable property purchased before 2001.
As explained in the article It is advisable to get the valuation of the property done from the registered valuer.
Typically its word of mouth or search in google. Many companies like governmentapprovedvaluers.com do it in Delhi and ZippServ in Bangalore, Pune.