As per the Budget presented by Finance Minister Arun Jaitley on 1 Feb 2017, the tax rate for those earning up to Rs 5 lakh is reduced to 5% and flat Rs 12,500 rebate offered to all taxpayers. But tax compliance will become stricter and delays in filing tax returns will cost money. This article gives Overview of Income Tax for FY 2017-18 AY 2018-19 applicable for income earned from 1 Apr 2017 to 31 Mar 2018, Income Tax Slab Rates for FY 2017-18 or AY 2018-19, Comparison of Calculation of Income Tax for FY 2016-17 and FY 2017-18
Table of Contents
Overview of Income Tax for FY 2017-18 AY 2018-19
This will be applicable, if passed, from 1 Apr 2017 to 31 Mar 2018.
Quote PAN for deals or pay fine at double the rate: Any recipient failing to quote his PAN will have to pay tax at double the rate mentioned in the relevant Section, or at the rate of 5%, whichever is higher
- The Budget has also proposed stricter rules for not filing tax returns on time. There will be a fee of 5,000 if the tax return is filed after the due date, but before 31 December of the assessment year. If filed after that, the fee will be 10,000. However, if the annual income of the taxpayer is up to 5 lakh, the fees will be lower at 1,000.
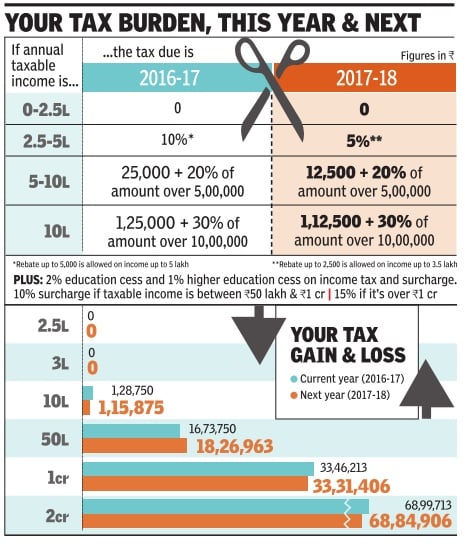
- The tax rate for those earning up to 5 lakh has been reduced from 10% to 5%, a move that will affect nearly two crore taxpayers.The tax rebate enjoyed by this segment of taxpayers under Section 87 has been reduced from 5,000 to 2,500 and will apply only to incomes up to 3.5 lakh.
- The tax rebate enjoyed by this segment of taxpayers under Section 87 has been reduced from 5,000 to 2,500 and will apply only to incomes up to 3.5 lakh.For other taxpayers, the Budget has offered a flat tax rebate of 12,500. If you add the savings on education cess, most taxpayers will save 12,875. Those earning over 1 crore will save over 14,000.However, upper
- For other taxpayers, the Budget has offered a flat tax rebate of 12,500. If you add the savings on education cess, most taxpayers will save 12,875.
- Those earning over 1 crore will save over 14,000.However, upper-middle-class taxpayers earning between 50 lakh and 1 crore will shell out more tax due to the 10% surcharge on tax.
- Simplification of the Income Tax Return form for income up to 5 lakh. This ITR form will now be a one-page document, very similar to the Saral form introduced several years ago. The finance minister also said that anyone filing tax returns for the first time will not attract scrutiny. This might induce individuals to start filing their tax returns.
- Salaried taxpayers who fudge house rent receipts will now find it difficult to claim exemption for housing rent allowance. The budget proposes to make it mandatory for TDS to be deducted if the rent exceeds 50,000 a month. Three years ago, it was made mandatory to mention the landlord’s PAN if the rent exceeded 1 lakh a year. Now, with the TDS requirement, it will become even more difficult to submit fake rent receipts to claim tax exemption.
- There is No Change in 80C limit It is still Rs 1.5 lacs. The investment in NPS or National pension scheme gives you extra tax deduction of up to Rs 50,000
- NO RGESS Tax exemption from FY 2017-18 Tax exemption under section 80CCG for RGESS (Rajiv Gandhi Equity Scheme) would NOT be available from FY 2017-18 on wards. The deduction was introduced in Budget 2012 to encourage retail participation in stock market but failed to take off as desired.
- Tax-exemption to partial withdrawal from NPS Partial withdrawal up to 25% of the contribution made by an employee would be exempted from tax.
Income From House Property
- Interest deduction on rented property capped at Rs 2 Lakh.Tax break due to interest paid on rented homes (whether first or second) will now be capped at 2 lakh. This is likely to impact investment in real estate.
Interest on Home Loan for the first-time buyer can be availed under section 80EE
For Loan of amount 35 lakh or less sanctioned for the first-time buyer between 01.04.2016 to 31.03.2017 with the value of house of 50 lakh or more. You can claim the additional interest of Rs 50,000 over and above 2 lakh (under section 24 of the income tax act) for FY 2017-18 or AY 2018-19.
- Section 80EE allows tax benefits for first time home buyers introduced in FY 2016-17. Income tax deduction can be claimed on home loan interest.The deduction allowed under this section is for interest paid on home loan up to maximum Rs 50,000 per financial year. You can claim this deduction until you have fully repaid the loan.
- The deduction under this section is available only to Individuals.
- This deduction is over and above the Rs 2 lakhs limit under section 24 of the income tax act.
- To claim this deduction loan must have been taken from a financial institution for purchasing your first residential house property.
- This is the 1st house you have purchased
- Value of this house is Rs 50 lakhs or less
- Loan taken for this house is Rs 35 lakhs or less
- Loan has been sanctioned by a Financial Institution or a Housing Finance Company
- As on the date of sanction of loan no other house is owned by you
Income from Business
- Professionals, salaried employees and smaller businessmen paying more than 50,000 a month as rent will have to deduct tax at source at 5%
- Reduced tax rate of 25% on firms with turnovers upto 50 cr in FY 2015-16 Period for carry-forward and use of MAT credit in creased from 10 to 15 years
- Beneficial withholding tax rate of 5% on interest on ECBs of Indian firms extended by three yrs till June 2020. Also extended to their rupee-denominated bonds
- Tax holiday to start-ups now available for 3 out of 7 yrs instead of existing 3 out of 5 yrs
Capital Gains for FY 2017-18 AY 2018-19
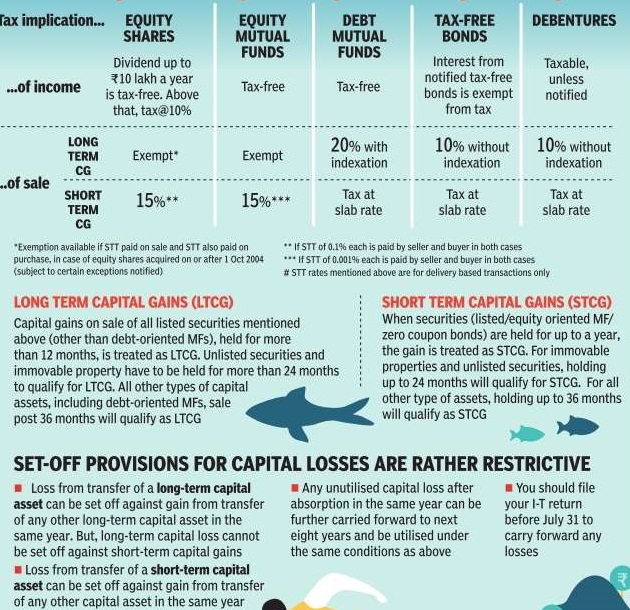
- Change of Base year for Indexation: For calculation of indexation in case of Long Term capital gains for all assets, the base year has been changed from April 1, 1981 to April 1, 2001.
- Budget 2017 changed the holding period for property to 2 years (from 3 years earlier) to qualify for Long Term Capital gains. This would lead to lower taxes.
- Long term capital gains on shares would only be available if securities transaction tax (STT) was paid while acquisition of shares. This will apply to all shares acquired after October 1, 2004. However this does not include bonus shares or shares allotted during IPO (initial public offer) or FPO (follow- on public offer). It would impact ESOPs, etc.
- Reinvestment of capital gains in notified redeemable bonds beyond NHAI, REC to qualify for long-term CG tax exemption. Currently, to save long term capital gains one could only invest in National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) or Rural Electrification Corporation Ltd (REC) bonds where you can park up to Rs 50 lakhs . Budget 2017 has proposed more options. More details are awaited.
- Following images shows Tax implications on various investments
Income Tax Slab Rates for FY 2017-18 or AY 2018-19
In AY 2017-18 or FY 2016-17, there were three slabs — 10 percent income tax for annual income between Rs 2.5 lakh and Rs 5 lakh, 20 percent on annual income from Rs 5 lakh to Rs 10 lakh, and 30 percent on income above Rs 10 lakh. This will be applicable, if passed, from 1 Apr 2017 to 31 Mar 2018. Our article Income Tax for AY 2017-18 or FY 2016-17 discusses Income Tax for income earned between 1 Apr 2016 to 31 Mar 2017.
| TAX | MEN and WOMEN below 60 years | SENIOR CITIZEN(Between 60 yrs to 80 yrs) | For Very Senior Citizens(Above 80 years) |
| Basic Exemption | 250000 | 300000 | 500000 |
| 5% tax | 250001 to 300000 | – | – |
| 5% tax | 300001 to 500000 | 300001 to 500000 | – |
| 20% tax | 500001 to 1000000 | 500001 to 1000000 | 500001 to 1000000 |
| 30% tax | above 1000000 | above 1000000 | above 1000000 |
|
|||
Comparison of Calculation of Income Tax for FY 2016-17 and FY 2017-18
The following images shows the Comparison of Income Tax Calculation in FY 2016-17 and FY 2017-18.
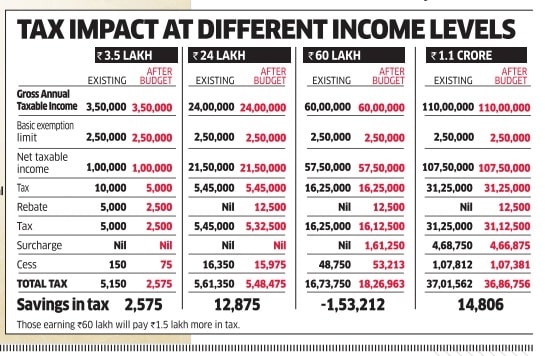
The following images what is tax impact at different income levels between FY 2016-17 and FY 2017-18. This will be applicable, if passed, from 1 Apr 2017 to 31 Mar 2018.
Related Articles:
Income Tax for AY 2017-18 or FY 2016-17




Good info about Income Tax… Thanks
there is no cost of inflated index.
80 EE is not applicable for ay 2018-19?? PLease confirm!
Section 80EE is applicable for Loan of amount 35 lakh or less sanctioned for the first-time buyer between 01.04.2016 to 31.03.2017 with the value of house of 50 lakh or more. You can claim the additional interest of Rs 50,000 over and above 2 lakh (under section 24 of the income tax act) for FY 2017-18 or AY 2018-19.
Sir,
If loan sanctioned after 31.3.2017??
80EE is not be applicable from FY 2017-18