Every country has a Central Bank. A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is an institution that oversees the banking system of the country, manages country’s currency, money supply, and interest rates. Central Bank of India is the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Just as the teachers and students in a school are supervised by a Principal, similarly all the banks of a country are supervised by the Central Bank. Central Bank of India is called Reserve Bank of India or RBI. “I don’t deal with RBI“, you must be thinking. But RBI or Central Bank always deal with you. Central Bank policies affect nearly all aspects of life, though people generally do not realise it. Every single thing that RBI does has an impact on the entire country. From the poorest farmer to the richest businessman. Newspaper typically talk about whether RBI should increase or decrease interest rate and Govt and RBI working together. You deal with RBI as it’s RBI Governor signature on the Indian note as shown in the image above.
We shall read about Jobs of Central Bank, answers the question why does RBI or Central Govt can’t print more money? How does Central bank or RBI decide how much money should be in the country?Explains case of Zimbabwe where the country printed lots of money, a currency note of trillion dollars and still people suffered. And then talk about Banks in India and Reserve Bank of India with a good and simple video and also RBI Comic Book for KKids explaining about how RBI makes sure that country grows.
Table of Contents
Jobs of the Central Bank
The Central Bank is the supreme monetary and banking authority in the country. Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central bank of India ( and is different from the bank Central Bank of India). It is called the Reserve Bank’ as it keeps the reserves of all commercial banks of India. Central banks in most nations are institutionally designed to be independent of political interference but…
The various jobs of Central Banks or RBI are
- It is the issuer of the currency. Our notes are signed by Governor of Reserve Bank of India.
- Acts as the Banking regulator: It lays down rules and regulations for various banking activities such as a loan, credit cards or debit cards
- Acts as a “lender of last resort” to the banking sector during times of financial crisis.
- Manages the Foreign Exchange
- Acts as the banker to the Government.
This video explains beautifully what does the Reserve Bank of India do?
Why doesn’t RBI or Central Bank print more money?
In one technical word Inflation! The price of any product is largely determined by its demand and supply. More the demand more costly it is, so as the demand rises so does the price and vice versa.
What will happen if the RBI/government prints money and gives it out to its citizens? The income of citizens will rise and most of us will spend on things. Say we all decide to go to the video game theatre where each game is prices Rs 100. First, only 10 people show up but slowly the queue becomes larger. But the number of video game machines did not increase. The owner cannot just buy more video games machines and put it as he has to think of how much more will people play and where will he put the machines. So the number of machines remains exactly the same. So the video parlour owner increases the price of each game to Rs 150, then to Rs 200, then to Rs 300. Some people can now not afford to play the game.
When too much money chases too few things price of things goes up. That’s inflation and it hurts everyone but poor people more as they have to earn daily and don’t have much money to save.
https://bemoneyaware.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/rbi-central-bank-demand-supply.jpg
When there is inflation the Central Bank or RBI increases the interest rates, so people reduce their borrowing from the bank. RBI also removes excess money from the market. Slowly demand goes down and so does the price. So it maintains price stability by controlling the money available to the people and by increasing or decreasing the interest rates.
How does Central bank or RBI decide how much money should be in the country?
The amount of money and the amount of goods and services produced in the economy determines the value of the money.
Suppose you have got 1 banana and 6 apples, let’s say 1 banana is worth 6 apples.
If you get another banana what do you have now? 2 bananas and 6 apples. And, therefore, 1 banana now becomes worth 3 apples. So if the number of bananas increased without increasing the apple, the value of each banana will fall. Just replace banana with currency and apples with the goods and services in the country.
That’s why Central Banks worldwide have strict regulations on how much money they want to print and keep it in balance with the total amount of goods and services produced in the country.
If the amount of currency in the economy is increased without the country producing enough goods and services, the value of its currency falls. This is called inflation. So, printing money is not the way to become rich, becoming competitive producing cheaper goods, and facilitating exports are. A little bit of inflation is acceptable, or rather desirable for any economy as it boosts growth. Most countries try to maintain their inflation rate at around 2-7%.
Zimbabwe printed more money and Suffered
Zimbabwe had a period of currency instability that began in the late 1990s. At the height of inflation in 2008-2009, People had to carry a bagful of money to buy a loaf of bread. Cost of a cup of coffee was trillions of dollars! In fact, Zimbabwe printed a currency of One hundred trillion dollars i. e 1 followed by 14 zeros. In 2009, Zimbabwe has to stop printing its currency and started using currencies of other countries. In 2015, Zimbabwe completely switched to the United States dollar.

trillion dollar Zimbabwe note
Here’s a picture of a kid going to buy groceries See the denomination on those notes?

Zimbabwe Kids with lots of worthless currency
If the amount of currency in the economy is increased without the country producing enough goods and services, the value of its currency falls. This is called inflation But Zimbabwe faced inflation of 500,000,000,000%..!!!!! and this is called Hyperinflation.
Banks and Reserve Bank of India
There are different kinds of banks in India. One way to classify it as Public sector banks, Private Sector Banks, Foreign banks etc. The various types of banks in India are as follows.
- Public sector banks, for example State Bank of India, Bank of India, Punjab National Bank etc. Public sector banks are those which are operated by government bodies.
- Private sector banks, for example ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank, ING Vysya Bank. Private sector banks are the banks which are controlled by the private lenders with the approval from the RBI.
- Foreign banks, for example, HSBC, Deutsche Bank. These banks offer banking services but are actually branches of banks of other countries, for example, HSBC is Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation. It is headquartered in England and is Europe’s biggest bank
Commercial banks are the most important types of banks. The term ‘commercial’ carries the significance that banking is a business like any other business. In other words, commercial banks are essentially profit-making institutions. They collect deposits from the public and lend money to business firms (manufacturers), traders, farmers and consumers. Generally, the term ‘banks’ to refer to commercial banks.
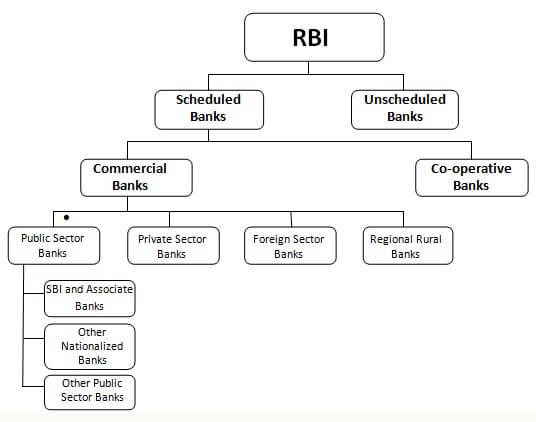
Types of Banks in India
The headquarters of the Reserve Bank of India is located in Mumbai. RBI has 19 regional offices most of them in state capitals and 9 sub-offices. It commenced its operations on 1 April 1935 to respond to economic troubles after the First World War. Following India’s independence on 15 August 1947, the RBI was nationalised on 1 January 1949.
How does RBI regulate Banks?
RBI acts as Banker to Banks, it lays down the broad parameters of banking operations in the country. It lays down rules and regulations of various banking activities like loans, credit cards or debit cards, branches, information that bank have to report, how to deal with Customers get KYC (Know Your customer)
The Reserve Bank continuously monitors operations of these banks to ensure that defaults do not take place, people can get their deposited money when required and people can get loans. As Banker to Banks, the Reserve Bank focuses on:
- Enabling smooth, swift and seamless clearing and settlement of inter-bank transactions, so that when you deposit cheque of one bank in another the money gets transferred.
- Providing an efficient means of funds transfer for banks
- The Reserve Bank stipulates minimum balances to be maintained by banks in these accounts so that people can continue to deposit and borrow from bank.
- Enabling banks to maintain their accounts with the Reserve Bank for statutory reserve requirements and maintenance of transaction balances.
- Acting as a lender of last resort : The commercial banks approach the Reserve Bank in times of emergency to tide over financial difficulties,but Reserve bank may rescue them though it might charge a higher rate of interest.
The image from the RBI book Money Kumar shows how the people need to trust the banks that it will keep its money safe.

How RBI makes sure bank work properly
Central Banks of Countries
Some of the central banks of other countries are as follows. The chief executive of a central bank is usually known as the Governor, President or Chair.
- United States – Federal Reserve System commonly referred to as “the Fed”
- The European Central Bank is the central bank for the euro and administers the monetary policy of the eurozone, which consists of 19 EU member states and is one of the largest currency areas in the world.
- United Kingdom: Bank of England
- Australia: Reserve Bank of Australia
- China (Mainland) – People’s Bank of China
There is no standard terminology for the name of a central bank,
Many countries use the “Bank of Country” form — for example, Bank of England (which, despite its name, is, in fact, the central bank of the United Kingdom as a whole, Bank of Japan.
The word “Reserve” is also often included, such as the Reserve Bank of India, Reserve Bank of Australia, Reserve Bank of New Zealand, the South African Reserve Bank, and Federal Reserve System.
Some central banks are called national banks, such as the Swiss National Bank, National Bank of Poland and National Bank of Ukraine
Some central banks are known as monetary authorities such as the Saudi Arabian Monetary Authority, Hong Kong Monetary Authority, Monetary Authority of Singapore, Maldives Monetary Authority and Cayman Islands Monetary Authority.
Some central banks may incorporate the word Central, for example, European Central Bank, Central Bank of Ireland, Central Bank of Brazil
Some central call themselves state banks such as the State Bank of Pakistan and State Bank of Vietnam.
Philippines central bank name is in its native language,Filipino, and is called Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas is used even in English.
YouTube Video on What does the Reserve Bank of India do?
This 5 minute YouTube video shows what does the RBI do?
Video on Should Central Banks be independent?
Donald Trump isn’t the only leader complaining about central bank policies. Italy, India, Turkey and Argentina are just a few of the countries seeing leaders pushing back against central bank independence – and some are succeeding. CNBC’s Silvia Amaro walks us through the events that led to central banks gaining their independence and whether that autonomy could be at risk.
RBI Book Money Kumar
RBI has come out with a book for school kids Money Kumar & The Monetary Policy which you can read here

RBI Money Kumar and monetary policy
Related Articles
- History of Money : How Money has evolved from Barter to Bitcoins
- Security Features in Indian Notes, International Notes
- Monuments on The Indian Notes: Konark Temple, Himalayas,Manglayan Mission
- Coin: Anatomy, Indian coins, Motto, History, Mint Marks





Grate information bro, very good information and keep posting
In BSNL, Pension Contribution, Medical Allowance reimbursement, CCA or City Compensatory Allowance, Dearness Allowances are other perks and benefits provided by BSNL to its employees are the best available options, every employee can check all their benefits through BSNL ERP Login portal called as ESS services.
There is a central organization which looks into this matter of UAN Login and it is called EPFO (Employees Provident Fund Organization). In India, it is mandatory to register any company with the EPFO, if the company has more than 20 employees.
ohh nice.. this article is also very informative for students who are preparing for banking exams..
Thanks
Informative post. Learnt a few things. Keep writing.
Thank you for encouraging words
Nice information Keep writing!
Thanks